1 Introduction
In order to optimize the manufacturing process and to further reduce current consumption, an optimized version of ATmega32 has been introduced.
The ATmega32A is a functionally identical, drop-in replacement for the ATmega32.All devices are subject to the same qualification process and same set of production tests, but as the manufacturing process is not the same some electrical characteristics differ.
ATmega32 and ATmega32A have separate datasheets. This application note outlines the differences between the two devices and the datasheets. There is also a detailed change log to assist the user at the end of the ATmega32A datasheet. Remember to always use the latest revision of the device datasheet.
Minor differences in typical characteristics are not discussed in this document as long as the low and high limits remain the same. For detailed information about the typical characteristics, see sections “Electrical Characteristics” and “Typical Characteristics” of the device datasheets.
Note: This application note serves as a guide to ease migration. For complete device details, always refer to the most recent version of the ATmega32A datasheet.
2 Changes in Characteristics
This section outlines such differences in characteristics that may have an effect on the application in which the device is used. For detailed information, refer to the most recent version of the device data sheets.
2.1 Current Consumption
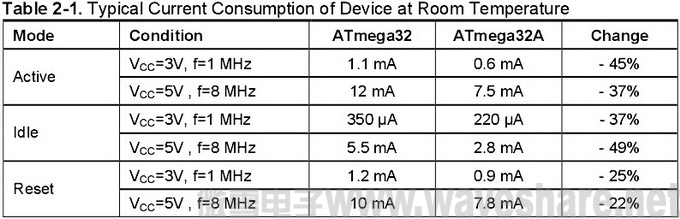
Active and Idle mode current consumption of the device has been reduced significantly. The tables below present typical current consumption figures at room temperature. All values are taken from device datasheets, unless otherwise noted.
2.2 Reset Pull-Up
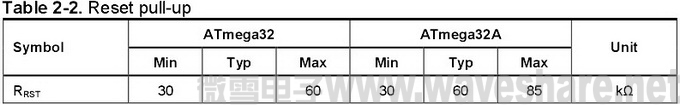
Table 2-2 summarizes the differences between the reset pull-up of ATmega32 and that of ATmega32A.
3 Datasheet Changes
For a summary of changes, see the revision history at the end of the ATmega32A datasheet.